Lithium-ion batteries are widely used because of their light weight, large capacity, and no memory effect—many digital devices today use lithium-ion batteries as power sources, although they are relatively expensive. Lithium-ion batteries have high energy density, their capacity is 1.5 to 2 times that of nickel-metal hydride batteries of the same weight, and they have a very low self-discharge rate. In addition, lithium-ion batteries have almost no "memory effect" and the advantages of no toxic substances are also important reasons for their widespread use.
Please pay attention to the safety of lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are prone to short circuits during charging. While most Li-ion batteries come with protection circuits against short circuits, there are also explosion proof cords. But this circuit may not necessarily be useful in various situations. The use of explosion-proof wire is also limited. So, what conditions should lithium-ion batteries meet in terms of safety performance?
Safety Features of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Regarding the assessment indicators of the safety performance of lithium-ion batteries, very strict standards are stipulated internationally. A qualified lithium-ion battery should meet the following conditions in terms of safety performance:
1. Short circuit: no fire, no explosion
2. Overcharge: no fire, no explosion
3. Hot box experiment: no fire, no explosion (150℃ constant temperature for 10min)
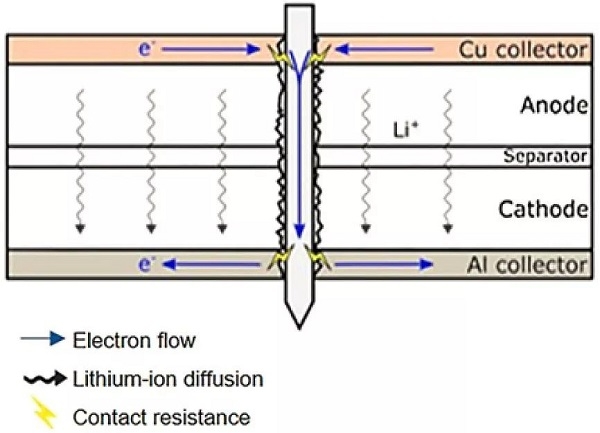
4. Needle prick: no fire, no explosion (penetrate the battery with Ф3mm nails)
5. Flat impact: no fire, no explosion (10kg weight hits the battery from a height of 1M)



